Next.js Data Fetching with Apollo Client
This example demonstrates various approaches to integrate WordPress as a headless CMS with a Next.js frontend using Apollo Client. It showcases different data fetching strategies, state management techniques, and modern web development patterns in a real-world application context.
Features
Section titled “Features”-
Covers various rendering patterns of Next.js
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR) for dynamic pages
- Static Site Generation (SSG) for static pages
- Client-Side data fetching (CSR) for blog settings
- Hybrid data fetching, combining SSR and CSR
-
Blog features
- Listing posts with pagination
- Live search of posts
- Fetching posts and pages using nodeByUri of WPGraphQL
- Fetching static pages at build time
- Commenting posts
- Header with dynamic blog title
-
Apollo Client integration
- Relay-style pagination
- Fragment management
- Error handling
- Custom fetch policies
- Custom error policies
- useLazyQuery example
- useMutation example
- Automatic Persisted Queries
Screenshots
Section titled “Screenshots”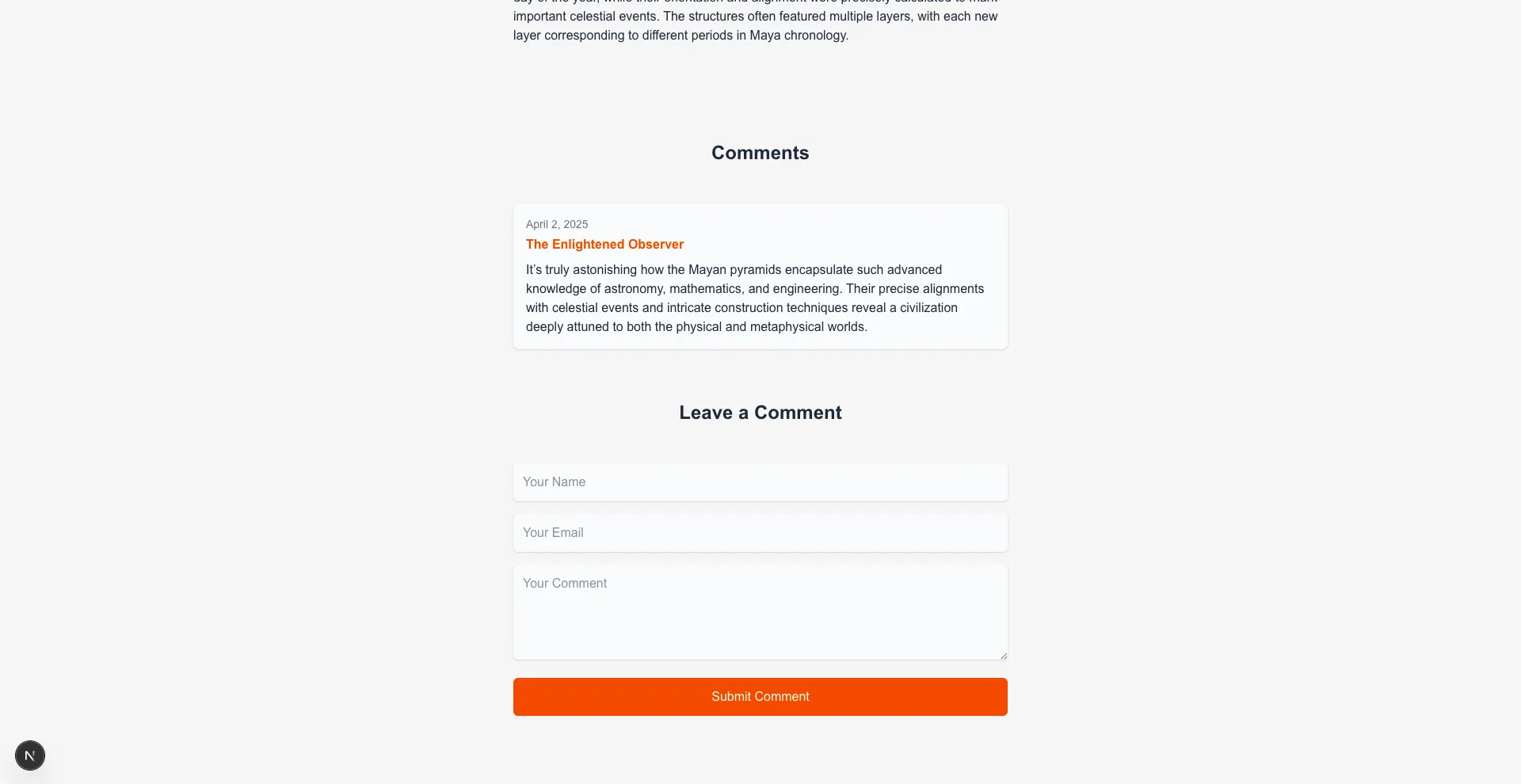 Post with comments | 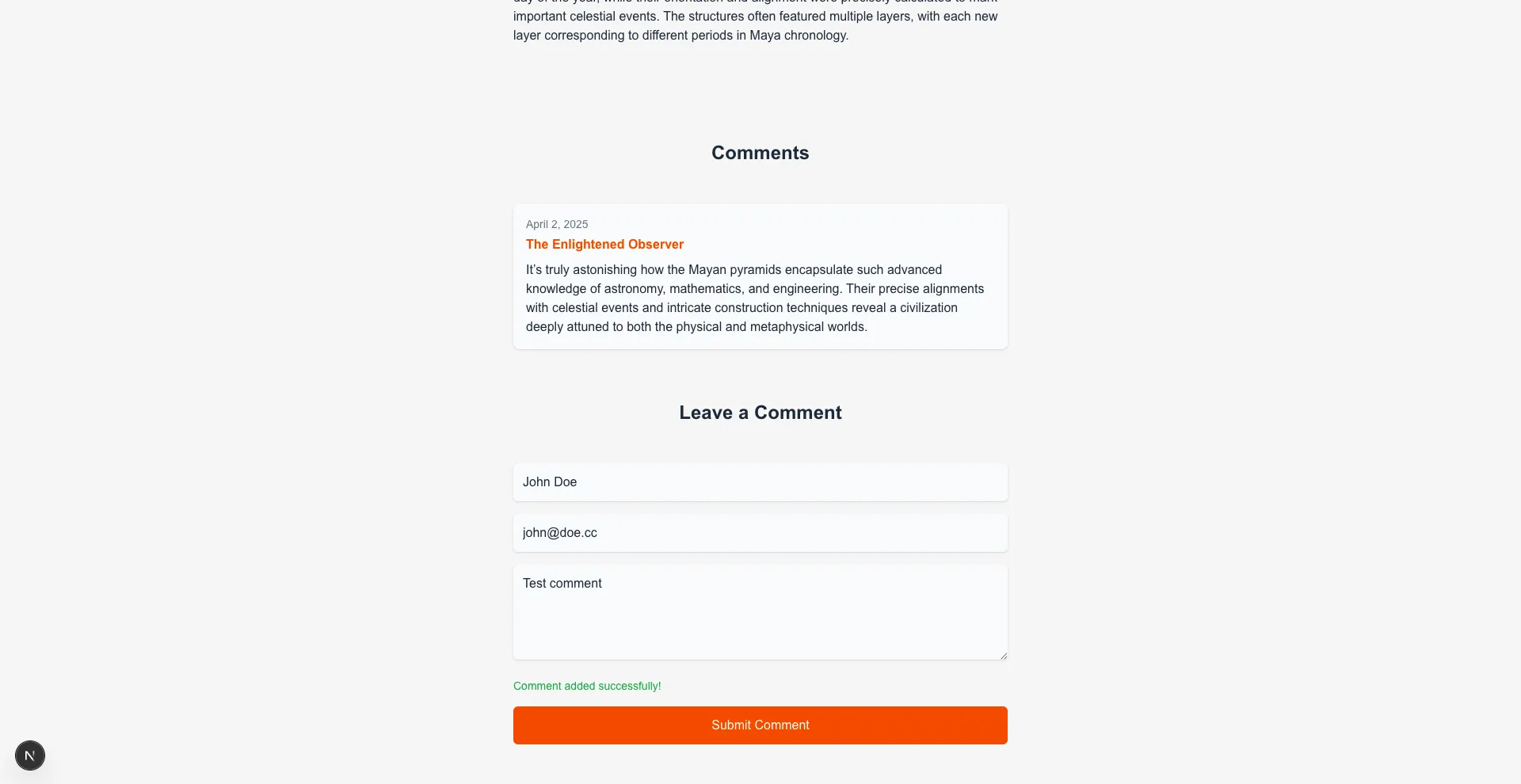 New comment | 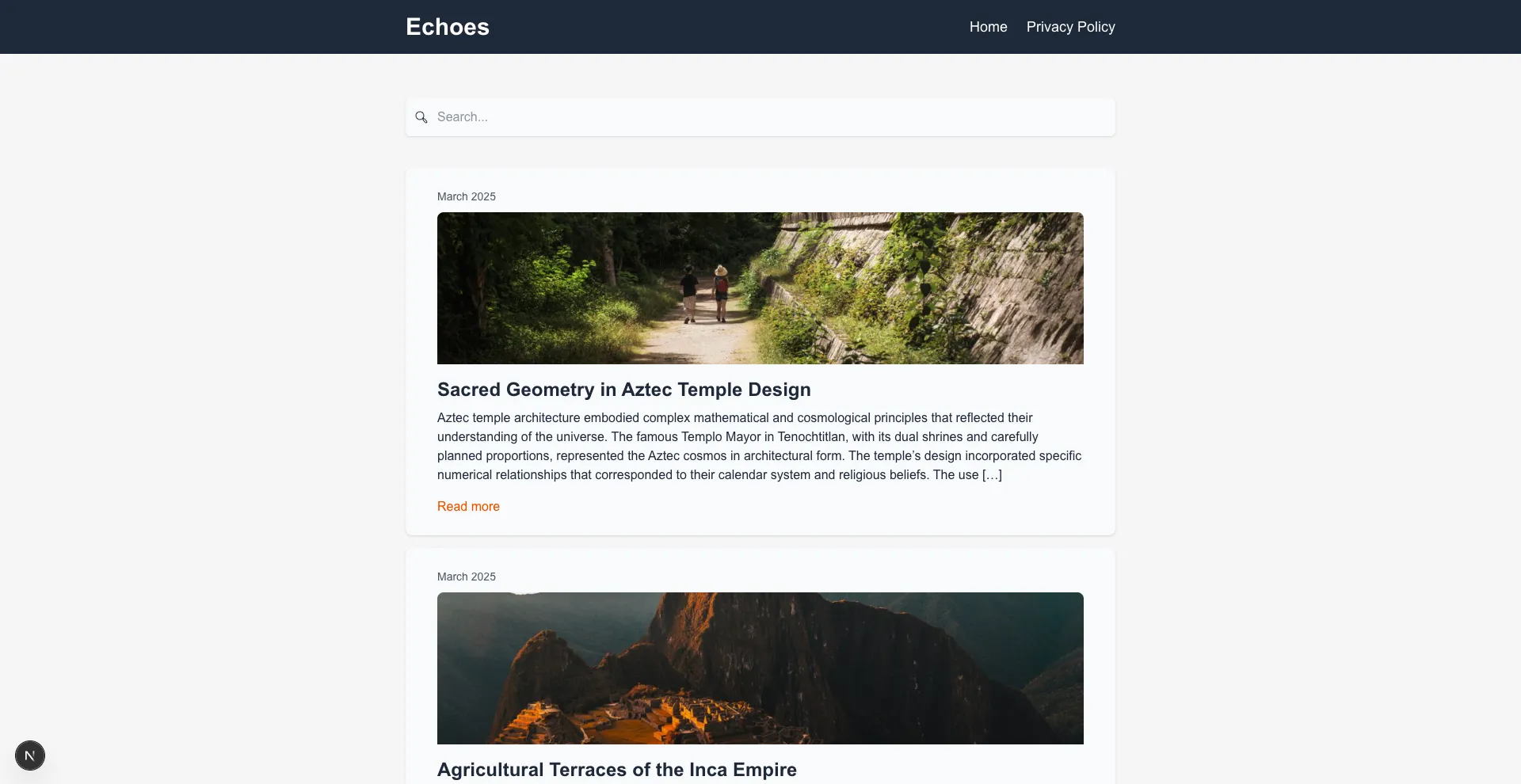 Home |
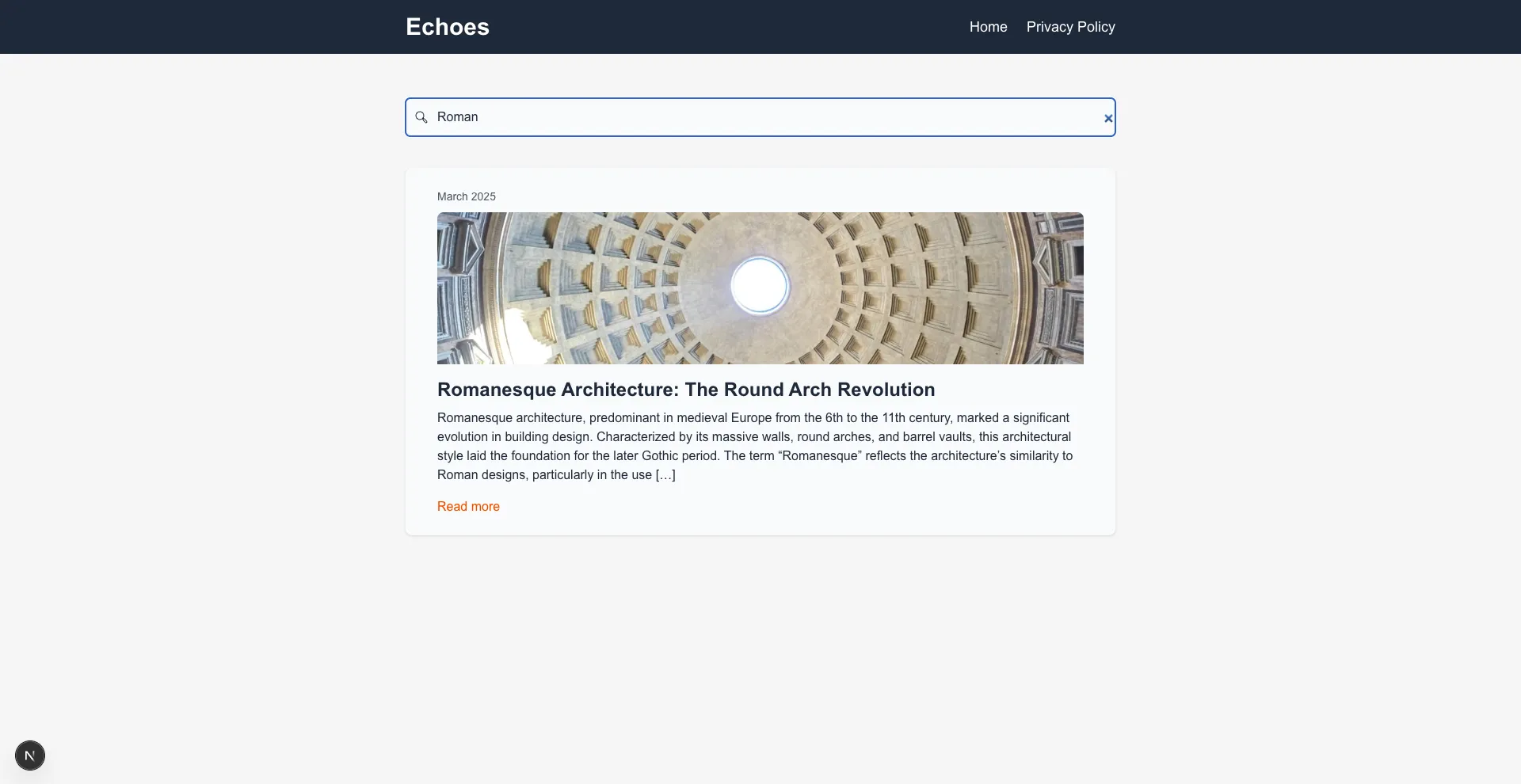 Live search |  Static page |  Load more |
Project Structure
Section titled “Project Structure”├── example-app│ └── src│ ├── components # React components│ ├── lib│ │ └── client.js # Apollo Client instance│ └── pages│ ├── [uri].js # Catch-all route for posts and pages│ ├── index.js # Home page│ └── privacy-policy.js # Statically generated page route├── .wp-env.json # wp-env configuration file└── wp-env ├── db │ └── database.sql # WordPress database including all demo data for └── setupRunning the example with wp-env
Section titled “Running the example with wp-env”Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”- Node.js (v18+ recommended)
- Docker (if you plan on running the example see details below)
Note Please make sure you have all prerequisites installed as mentioned above and Docker running (docker ps)
Setup Repository and Packages
Section titled “Setup Repository and Packages”- Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/wpengine/hwptoolkit.git - Install packages
cd hwptoolkit && npm install - Setup a .env file under
examples/next/apollo-client-data-fetch/example-appand add these values inside:
NEXT_PUBLIC_WORDPRESS_URL=http://localhost:8888NEXT_PRIVACY_POLICY_URI=/privacy-policyor run the command below:
echo "NEXT_PUBLIC_WORDPRESS_URL=http://localhost:8888\\nNEXT_PRIVACY_POLICY_URI=/privacy-policy" > examples/next/apollo-client-data-fetch/example-app/.envBuild and start the application
Section titled “Build and start the application”cd examples/next/apollo-client-data-fetch- Then run
npm run example:buildwill build and start your application. - This does the following:
- Starts up wp-env
- Imports the database from
wp-env/db/database.sql - Install Next.js dependencies for
example-app - Runs the Next.js dev script
Congratulations, WordPress should now be fully set up.
| Frontend | Admin |
|---|---|
http://localhost:3000/ | http://localhost:8888/wp-admin/ |
Note: The login details for the admin is username “admin” and password “password”
Command Reference
Section titled “Command Reference”| Command | Description |
|---|---|
example:build | Prepares the environment by starting WordPress, importing the database, and starting the application. |
example:dev | Runs the Next.js development server. |
example:dev:install | Installs the required Next.js packages. |
example:start | Starts WordPress and the Next.js development server. |
example:stop | Stops the WordPress environment. |
example:prune | Rebuilds and restarts the application by destroying and recreating the WordPress environment. |
wp:start | Starts the WordPress environment. |
wp:stop | Stops the WordPress environment. |
wp:destroy | Completely removes the WordPress environment. |
wp:db:query | Executes a database query within the WordPress environment. |
wp:db:export | Exports the WordPress database to wp-env/db/database.sql. |
wp:db:import | Imports the WordPress database from wp-env/db/database.sql. |
Note You can run
npm run wp-envand use any other wp-env command. You can also see https://www.npmjs.com/package/@wordpress/env for more details on how to use or configurewp-env.
Database access
Section titled “Database access”If you need database access add the following to your wp-env "phpmyadminPort": 11111, (where port 11111 is not allocated).
You can check if a port is free by running lsof -i :11111